Identity Stitching
Before reading this section, its highly recommended to go through the Introduction. To recap, one of the main goal of PB is to take all data collected via RudderStack (first party sources like app, website as well as ETL data from SaaS applications) and create C360 (aka customer 360 view). Identity stitching is an important precursor step to building a C360 data.
At high level, all data in warehouse can be abstracted as unstructured objects but having one or more user(or entity, going forward in the doc we will use entity) identities. Example of possible entity identifiers:
Anonymous identifier, e.g GUID, device-id, cookie-id
Personal identifier, e.g email, name
Your system derived identifier, e.g you might have an internal system to generate and maintain identifier
In order to have a unified C360, its important to be able to correlate different entity identifiers as one so that all relevant data can be attributed to one entity.
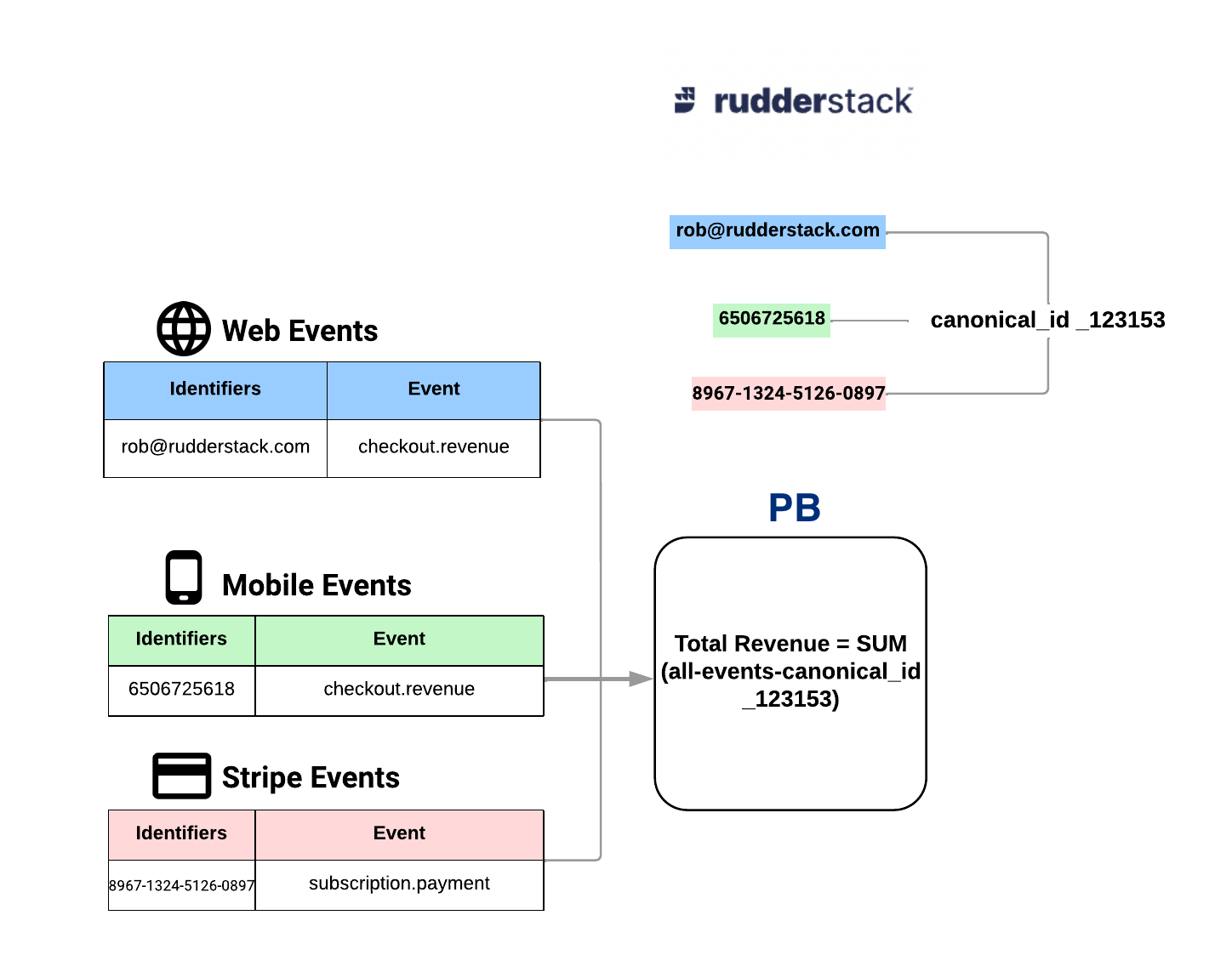
Picture of single identity created from different multiple identities
If put simply, this is a graph matching problem (further details can be read here). This document describes how to use RudderStack to enable ID stitching in a config driven approach for N number of data sources which has any identifier(s) data.
Default ID Stitcher in the Project
The section Project Layout gives high level structure of defining a PB project. This section will give a detailed walk through about how you can define an ID stitching model with example. Helpful comments have been added in sample yaml definitions below, but next section will detail about different fields in these files.
The pb_project.yaml file should define the entities supplied to the model. In case of ID stitching model, you need to define all identifiers from different data sources to be stitched as a canonical id ( aka main_id in the example).
# Project name
name: sample_id_stitching
# Project's yaml schema version
schema_version: 49
# Warehouse connection
connection: test
# Allow inputs without timestamps
include_untimed: true
# Folder containing models
model_folders:
- models
# Entities in this project and their ids.
entities:
- name: user
# optional: modelRef of custom ID stitcher model
# id_stitcher: models/sample_id_stitcher
id_types:
- main_id # You need to add ``main_id`` to the list only if you have defined ``main_id_type: main_id`` in the id stitcher buildspec.
- user_id # one of the identifier from your data source.
- email
id_types:
- name: main_id
- name: user_id
filters: # Multiple filters like exclude, include can be added using value or regex match.
- type: exclude
value: ""
- name: email
filters: # An include filter example to consider values matching provided regex. Note that this will automatically be anchored by sql to include the beginning and ending regex special chars (^ and $).
- type: include
regex: ".+@.+" # Automatically anchored, so equivalent to "^.+@.+$"
Now you need to define input for the entities above in your models/inputs.yaml file.
inputs:
- name: rsIdentifies
contract:
is_optional: false
is_event_stream: true
with_entity_ids:
- user
with_columns:
- name: user_id
- name: anonymous_id
- name: email
app_defaults:
table: rudder_events_production.web.identifies # one of the WH table RudderStack generates when processing identify or track events.
occurred_at_col: timestamp
ids:
- select: "user_id" # kind of identity sql to pick this column from above table.
type: user_id
entity: user # as defined in project file.
to_default_stitcher: true # if not defined then by default it's set to true.
- select: "anonymous_id"
type: anonymous_id
entity: user
- select: "lower(email)" # can use some sql as well, example of a complex sql will be added in later section.
type: email
entity: user
- name: rsTracks
contract:
is_optional: false
is_event_stream: true
with_entity_ids:
- user
with_columns:
- name: user_id
- name: anonymous_id
app_defaults:
table: rudder_events_production.web.tracks # another table in WH maintained by RudderStack processing track events.
occurred_at_col: timestamp
ids:
- select: "user_id"
type: user_id
entity: user
- select: "anonymous_id"
type: anonymous_id
entity: user
By default, ID stitcher edges are specified using all the defined input source tables and packages. This way, ID Stitcher edges can be defined across multipe projects. ID Stitcher edges can also be defined on SQL models and pynative models.
Default ID Stitcher runs in incremental mode by default. The settings can be overridden in the project file. For example:
entities:
- name: user
id_types:
- test_id
- exclude_id
default_id_stitcher:
validity_time: 24h # 1 day
materialization:
run_type: discrete
enable_status: good_to_have
Note
Any column mentioned in IDs is automatically sent to the ID Stitcher, unless it’s overridden using to_default_stitcher: false.
Usage Details
For few of the configurations, this section will help with some examples to describe enhanced usage of ID stitching based on requirements.
Identifiers from multiple data sources
RudderStack’s configuration driven approach makes it very simple to consider multiple identifiers and tables. For example, all you need to do is three things in order as described in previous section:
Add entities in
pb_project.yamlrepresenting identifiers.Add references to table and corresponding sql in
models/inputs.yamlAdd table reference names defined in
models/inputs.yamlas edge_sources in in your model definition.
Leverage Sql Support
Sql in your models/inputs.yaml makes it very powerful enabling solution for multiple scenarios.
Say you want identity to be not individual email but as domain. For example, all internal users in your organization you want to tag as 1 entity. This you can accomplish by adding a sql to extract the domain part as identifier value:
lower(split_part({{email_col}}, '@', 2))
Custom ID Stitcher
If you wish customize the ID stitcher, kindly refer the section Custom ID Stitcher.
Well that’s all about ID stitching. We will keep updating this document as we keep building more things. This will help you to move to Entity Traits 360 about entity feature(s) model which builds your C360 data.